|
 Relative Permeability and
Water Cut
Relative Permeability and
Water Cut
Since we are interested in how much oil or gas will flow from
a well, and would rather not have any water flow, it is necessary
to calculate relative permeability and water cut to determine
how good a well might be.
Relative
permeability for water.
1: Krw = (Sw - SWir) / (1 - SWir)
Relative
permeability for oil.
2: Kro = (0.9 - Sw) / (0.9 - SWir)
Relative
permeability for gas.
3: Krg = (1 - (Sw - SWir) / (1 - SWir)) * (1 - ((Sw - SWir) /
(1 - Sw)) ^ 0.25 * Sw ^ 0.25)^0.5
Water
oil ratio.
4: KRwo = Krw / Kro
5: WOr = BO * (VISO / VISW) * (KRwo)
Water
gas ratio.
6: KRwg = Krw / Krg
7: WGr = BG * (VISG / VISW) * (KRwg)
Water
cut for oil wells.
8: WCo = WOR / (1 + WOR)
Water
cut for gas wells:
9: WCg = WGR / (1 + WGR)
Where:
BG = volume factor for gas (fractional)
BO = volume factor for oil (fractional)
Krg = relative permeability to gas (fractional)
Kro = relative permeability to oil (fractional)
Krw = relative permeability to water (fractional)
KRwg = water to gas permeability ratio (fractional)
KRwo = water to oil permeability ratio (fractional)
Sw = water saturation (fractional)
SWir = irreducible water saturation (fractional)
VISG = viscosity of gas (cp)
VISO = viscosity of oil (cp)
VISW = viscosity of water (cp)
WCg = water cut for gas well (fractional)
WCo = water cut for oil well (fractional)
WGr = water gas ratio (fractional)
WOr = water oil ratio (fractional)
 COMMENTS:
COMMENTS:
Charts for solving the relative permeability relationships and for water cut
below. Viscosity
data required for water-oil and water-gas ratio are also given for oil and gas.
Relative
permeability from log analysis without core data as a control
is probably pointless.
RECOMMENDED
PARAMETERS:
See Figures.
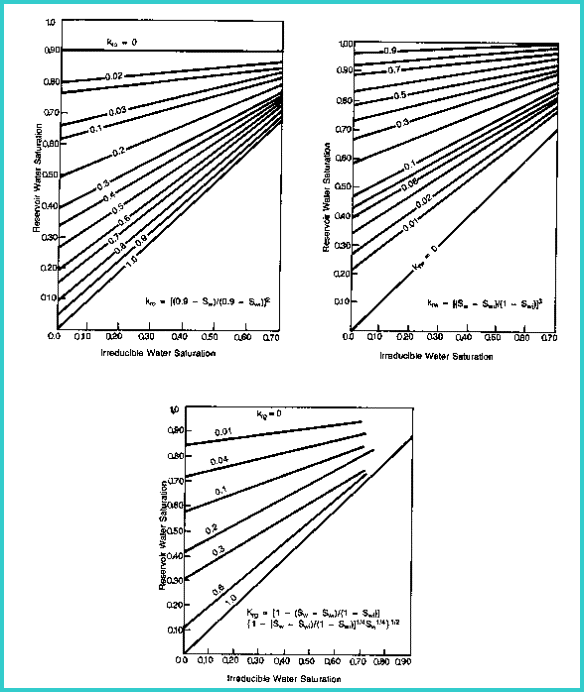
Relative permeability
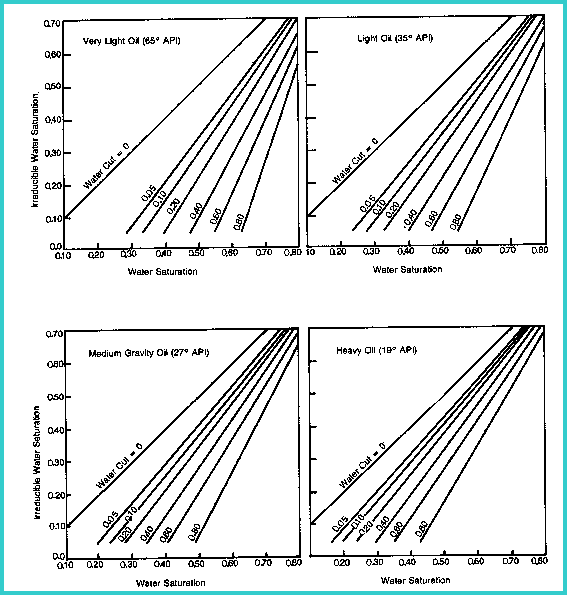
Water cut
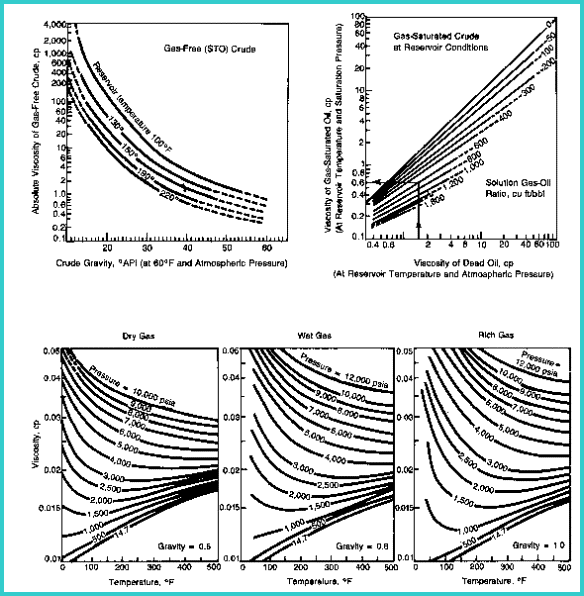
Viscosity
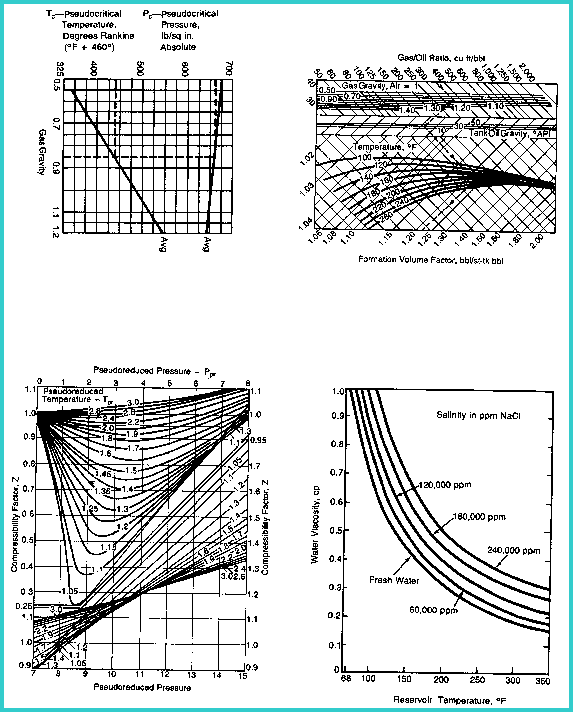
Viscosity of water and pseudo critical gas properties
 NUMERICAL
EXAMPLE:
NUMERICAL
EXAMPLE:
1. Assume data from Sand C
PHIe = 0.30
Sw = 0.50
PHIxSW = 0.06
SWir = 0.06 / 0.30 = 0.20
Krw = (0.50 - 0.20) / (1 - 0.20) = 0.375
Kro = (0.9 - 0.50) / (0.9 - 0.20) = 0.571
Krg = (1 - (0.5 - 0.3) / (1 - 0.2)) * (1 - ((0.5 - 0.3) / (1 -
0.5)) ^ 0.25 * 0.5 ^ 0.25) ^ 0.5
= (0.75 * (1 - 0.4 ^ 0.25 * 0.5 ^ 0.25) ^ 0.5 = 0.431
KRwo = 0.375 / 0.571 = 0.657
KRwg = 0.375 / 0.431 = 0.870
2.
Assume oil well data:
BO = 0.8
oil gravity = 40 degrees API
VISO = 1.2 cp
FT = 160 degrees F
VISW = 0.5 cp
| salinity = 120,000 ppm
WOr = 0.8 * (1.2 / 0.5) * 0.657 = 1.26
3.
Assume gas well data:
BG = 0.8
VISG = 0.015 cp
VISW = 0.5 cp
dry gas
pressure = 1800 psi
salinity = 120,000 ppm
WGr = 0.8 * (0.015 / 0.5) * 0.870 = 0.021
4.
Water Cut:
WCo = 1.26 / (1 + 1.26) = 0.557
WCg = 0.021 / (1 + 0.021) = 0.021
Thus,
if this is an oil zone, it will produce over 55% water on initial
completion. If it is a gas well, it will produce only 2% water.
|

