|
 Permeability from Porosity
Permeability from Porosity
This simple
regression of core porosity versus core permeability:
1:
PERMp = 10 ^ (HPERM * PHIe + JPERM)
2: IF PERMp > 20000
3: THEN PERMp = 20000
Where:
JPERM = permeability constant (fractional)
HPERM = porosity exponent (fractional)
PERMp = calculated permeability (millidarcies)
PHIe = effective porosity (fractional)
 COMMENTS:
COMMENTS:
Because a poor choice of HPERM could create very large values
of permeability, the computation is usually constrained to prevent
unreasonable answers. Results have been very good in low and high
porosity when calibrated to core.
You
can fit a regression line to anything - look at the graph and check
the R-squared to confirm that the regression line is rational.
 RECOMMENDED
PARAMETERS:
RECOMMENDED
PARAMETERS:
ROCK TYPE HPERM JPERM
Carbonates
chalky 10 - 20 -2.5
fine sucrosic or
intercrystalline 20 - 30 -2.5
coarse sucrosic or
intercrystalline 25 - 50 -2.5
small vuggy 30 - 100 -2.5
large vuggy 50 - 200 -2.5
fractures 200 - 300 -3.0
Sandstones
very
fine grains 10 - 20 -3.0
fine grains 15 - 25 -3.0
medium grains 20 - 30 -3.0
large grains 25 - 50 -3.0
conglomerate 20 - 50 -3.0
unconsolidated 20 - 50 -3.5
fractures 200 - 300 -3.0
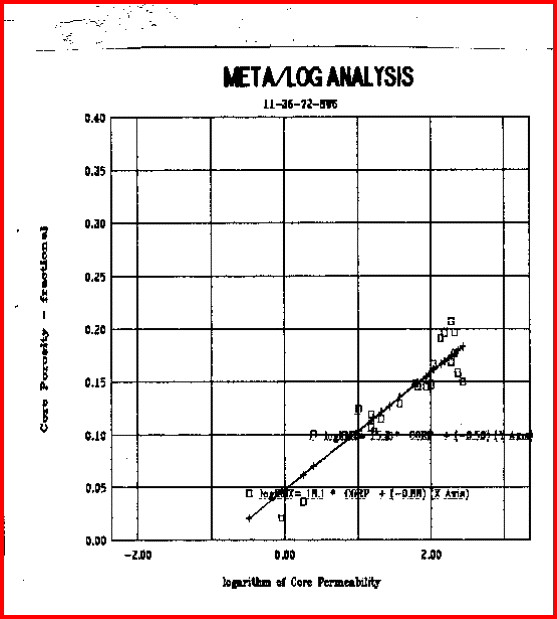
Permeability from Porosity - example of a "good" regression
line.
 NUMERICAL
EXAMPLE
NUMERICAL
EXAMPLE
Assume data from Classic Example Sand B.
PHIe = 0.30
SWir = Sw = 0.25
1.
Wylie-Rose formula / Morris-Biggs parameters:
CPERM = 62500
DPERM = 6.0
EPERM = 2.0
PERMw = 62500 * (0.30 ^ 6) / (0.25 ^ 2) = 730 md
2.
Wylie-Rose formula / Timur parameters:
CPERM = 3400
DPERM = 4.4
EPERM = 2.0
PERMw = 3400 * (0.30 ^ 4.4) / (0.25 ^ 2) = 272 md
 Permeability from Formation Factor
Permeability from Formation Factor
Since Formation Factor (F) is a function of porosity, F is also
a predictor of permeability:
4:
F = A / (PHIe ^ M)
5: PERMff = FPERM / (F ^ GPERM)
Where:
A = tortuosity exponent (fractional)
FPERM = permeability constant (fractional)
GPERM = porosity exponent (fractional)
F = formation factor (fractional)
M = cementation exponent
PERMf = calculated permeability (millidarcies)
PHIe = effective porosity (fractional)
 COMMENTS:
COMMENTS:
This formula has not been as successful as the Wylie - Rose approach.
 RECOMMENDED
PARAMETERS:
RECOMMENDED
PARAMETERS:
ROCK TYPE FPERM GPERM
Sandstone 7.0 * 10 ^ 6 4.5
Limestone 4.0 * 10 ^ 6 3.5
Data
from individual core studies varies considerably from these average
values.
 NUMERICAL
EXAMPLE
NUMERICAL
EXAMPLE
Assume data from Classic Example Sand B.
PHIe = 0.30
A = 0.62
M = 2.15
 Formation factor method:
Formation factor method:
FPERM = 7.0 * 10 ^ 6
GPERM = 4.50
F = 0.62 / (0.30 ^ 2.15) = 8.25
PERMf = 7.0 * 10 ^ 6 / (8.25 ^ 4.5) = 526 md
 META/LOG "PERM" Compare
Permeability Calculated from Various Methods
META/LOG "PERM" Compare
Permeability Calculated from Various Methods
Download this spreadsheet:
SPR-24 META/LOG PERMEABILITY CALCULATOR
Calculate and compare permeability derived from well
logs,
5 Methods.
|