|
 Editing Sonic Logs With SRS or VSP Data
Editing Sonic Logs With SRS or VSP Data
Seismic times obtained through the integration of a sonic log
usually differ from those obtained by means of a seismic pulse
(surface surveys or check shots) for many reasons. These range
from basic discrepancies between the two approaches to
disturbances in sonic readings caused by cycle skipping,
detection of mud arrivals in large holes, formation alteration,
and invasion.
Considerable effort has been dedicated in recent years to
alleviate this second category of problems. More powerful
transducers, sophisticated detection schemes, and long spacing
sondes have all led to higher quality logs. Nevertheless, sonic
logs are not yet completely free of anomalous effects and the
basic discrepancies mentioned above remain, particularly
invasion, which cannot be cured by tool design.
Seismic checkshot times are used as a reference to calibrate the
sonic log through a process called drift curve correction. The
drift curve is a log of the difference between integrated sonic
log time and check shot seismic time. When integrated sonic log
times are higher than seismic times (the usual case), drift is
negative.
Drift is made equal to zero at an arbitrary depth, the tie
point, often the top of the sonic log when, as it should be, a
checkshot is available at that depth. Drifts are plotted at each
shot depth. Then a curve is drawn, as segments of straight lines
fitting the drift points as well as possible. The junction of
two such segments is called a "knee". A knee should not be
necessarily located at a checkshot point, but where there is a
change of lithology or of sonic character.
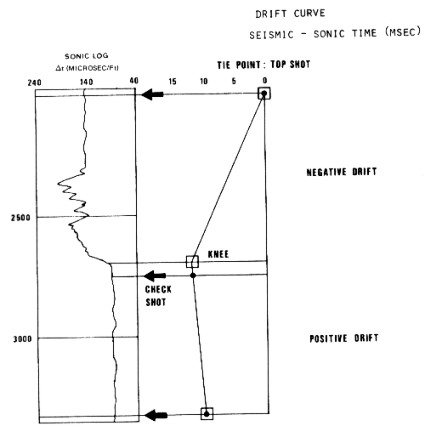
Plot of sonic log drift correction from checkshot survey
Between two consecutive knees, the sonic log is adjusted to get
rid of the drift. Two different methods are in use: block shift
method and delta-T minimum method. However, only one method
should be used on a given interval. After these adjustments, the
sonic log should provide the continuous formation transit time
in the undisturbed formation.
These methods work well where there is rock alteration near the
well bore, vuggy porosity, or long intervals of gas bearing
reservoir. If differences were caused by thin gas zones, or a
few bad spots or cycle skips on the log, it is unlikely that
either method will provide correct answers. This is due to the
fact that both methods apply a small correction over fairly
large intervals, instead of a large correction where it is
needed. Manual editing before applying these methods often works
very well.
If
there are many skips or large intervals of bad hole condition,
check shots will not directly cure the problem. Other methods,
such as those described in the next few Sections, will create a
better log, which can then be calibrated with checkshots or
vertical seismic profiles data.
 1.
Block Shift Method:
1.
Block Shift Method:
Calculate total drift between two knees:
1: D = (T2 - T1) * 1000
/ 2 - (Sum (DTCi * INCR)) / 1000
Calculate drift to apply to each data point:
2: C = 1000 * D / (H2 -
H1)
Apply constanr correction to all log data points between H1 and
H2:
3: DTCcor = DTC + C
Where:
C = drift correction constant
for each data point (fractional)
D = total drift between integrated sonic and seismic checkshot data (msec)
DTCi = individual sonic travel times between H1 and H2 (us/m or us/ft)
DTC = sonic travel time from
original log (us/m or us/ft)
DTCcorr = corrected sonic
travel time (us/m or us/ft)
H1, H2 = depths at two lnees on SRS plot (meters or feet)
T1,T2 = one-way times at two lnees on SRS plot (msec)
INCR = log digitizing interval (meters or feet)
The
block shift is used when drift is small and no single anomaly is
the cause of the error.
By
looking at the image below, one can see that a block shift will not
always be a satisfying correction. On that example, a long
spacing sonic agrees with checkshots and may be assumed to be
right. The standard sonic agrees with the long spacing over the
cleaner interval. A block shift correction will change the sonic
over that interval and impose changes which will generate false
reflections on a synthetic seismogram.
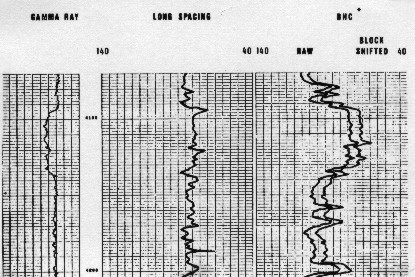
Block shifted sonic log - not recommended but
widely used
A
Delta-T minimum correction can be applied in such cases, when
the sonic log reading is too high and the difference of drifts
is big. Shale alteration or skipping are then suspected. A
threshold, DTMIN, is chosen: all values of sonic travel time
smaller than this threshold are assumed to be good and are not
corrected. When the sonic reading exceeds DTMIN, the excess of
the sonic value over the threshold is corrected by a reduction
factor defined for the interval.
 2.
Delta-T Minimum Correction Method:
2.
Delta-T Minimum Correction Method:
Calculate total drift between two knees on drift curve
4: D = (T2 - T1) * 1000
/ 2 - (Sum (DTCi * INCR)) / 1000
Calculate drift factor to apply to data
5: C = 1 + (D / Sum (DTCi
* INCR - DTCMIN * INCR) / 1000)
Apply correction if data is above DTCMIN
6: IF DTC > DTCMIN
7: THEN DTCcorr = C * (DTC
- DTCMIN) + DTCMIN
8: OTHERWISE DTCcorr =
DTC
Where:
C = drift correction constant for each data point (fractional)
D = total drift between integrated sonic and seismic checkshot data (msec)
DTCi = individual sonic travel times between H1 and H2 (us/m or us/ft)
DTC = sonic travel time from original log (us/m or us/ft)
DTCcorr = corrected sonic travel time (us/m or us/ft)
DTCMIN = sonic travel time below which data should be reliable (us/m
or us/ft)
H1, H2 = depths at two lnees on SRS plot (meters or feet)
T1,T2 = one-way times at two lnees on SRS plot (msec)
INCR = log digitizing interval (meters or feet)
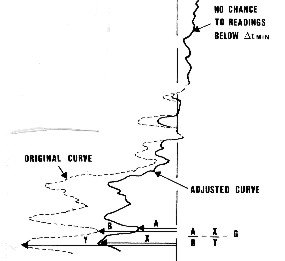
DELTA-T minimum correction applied to sonic
log
Other logs which are less affected by environmental effects
(neutron, deep resistivity) are generally used to determine the
zones over which the sonic readings are correct and hence to
choose the appropriate value of DTCMIN. It may vary with depth.
CAUTION: Neither of these methods will adequately correct a
sonic log in a gas zone. See below for details. A possible
exception is very closely spaced checkshots throughout the
entire gas interval, such as through the long gas filled tight
sands of the Deep Basin of Alberta.
|

