|
 Porosity - Lithology From Shear Seismic
Porosity - Lithology From Shear Seismic
Complex transmission and mode conversion phenomena occur at the
interface between two media, as compressional or shear wave energy
passes through it. When
a compressional wave strikes an interface, the incident energy
is distributed over four distinct waves:
1. transmitted compressional wave, Pt
2. reflected compressional wave. Pr
3. converted transmitted shear wave, PSt
4. converted reflected shear wave, PSr
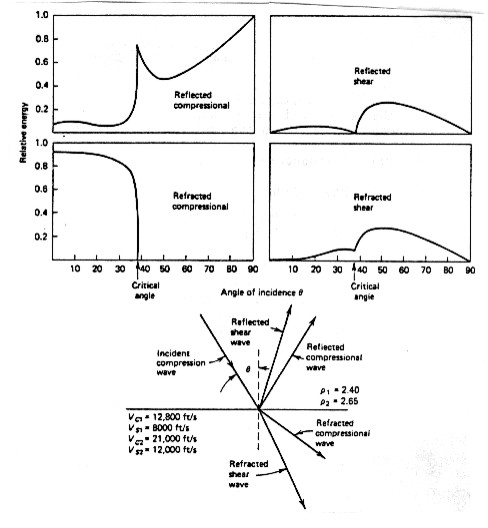
Reflected and transmitted wave modes
The
amplitude of each of these components versus incidence angle is
shown below. Notice the dramatic change in
reflected energy at angles above the critical angle.
If
an S-wave reaches the interface, converted S-waves, SPt and SPr,
are also created. For seismic surveys, SH is the component of
the shear wave (SPr) perpendicular to the vertical plane containing
the seismic line. SV is the component in the plane. The direction
of particle motion for the various modes is shown below.
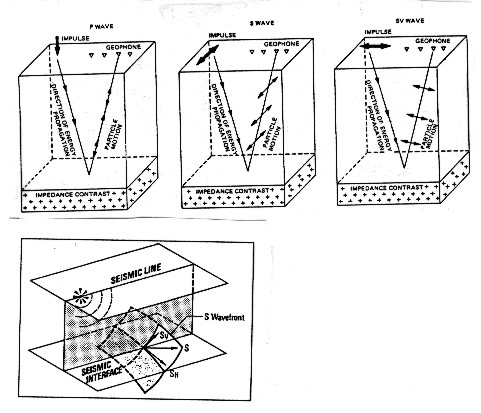
Reflected and transmitted wave modes
When
SH is in the interface plane, there is no conversion of SH-waves
into P- and SV-waves and inversely. This is why SH seismic records
are more simple as a rule than the P or SV records.
Interference
from shear waves on conventional CDP seismic stacking is avoided
by adequate velocity analysis, since shear waves are much slower
than compressional and have much higher normal moveout. The typical
velocity regime is shown below.
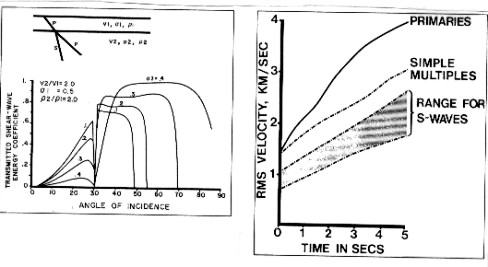
Shear amplitude and velocity
By
suitably gathering and velocity filtering seismic traces, the
compressional and shear arrivals can be separated from each other.
The interval velocity from compressional and shear sections can
be computed from the stacking velocity of each. Poisson's ratio
can be computed and displayed from:
_____1: PR = ((Vc / Vs)^2
- 2) / (2 * (Vc / Vs)^2 - 1)
|

